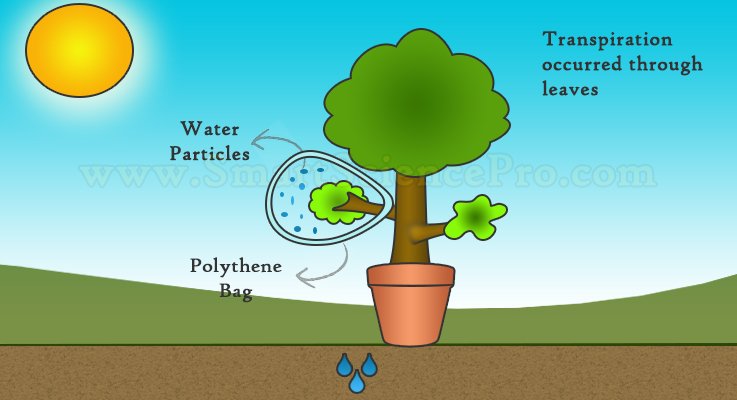
It’s no doubt that you have seen plants which have been wilted due to no water supply. If you pour some water to that wilted plant, it’d be revitalized. So exactly why plants face dearth of water? In science, it is a rule of thumb to do experiments to answer such WHYs …
Do you remember that we used a portable potted plant to test the 4 factors of photosynthesis? Similarly, we’re going to use a plant again for this experiment. Okay, select your plant and cover one of its twigs with a polythene bag. Let it be there for a few hours.
Then take the polythene bag out and put some Anhydrous Copper Sulphate to inside the bag. If you touch or look closer inside the polythene bag, you can see some liquid is there. Those Anhydrous Copper Sulphate in the bag will turn to blue by revealing that liquid is water. This experiments shows us that the plants are giving out water.
You can’t see the water coming out, because they are coming out in the form of vapor.
- The process of losing water from a plant as vapor is known as Transpiration.
- Stomata of the leaves are the main places that the transpiration occurs.
- Due to the usage of Stomata, it is known as Stomatal Transpiration.
- Another place is the cuticle of the plant leaf, it is known as Cuticular Transpiration.
- Other places are airpores in the roots and the stem of the plant, it is known as Airpore Transpiration.
You know what the amount of water coming out of the plant as vapor is very large – 95% of water taken into the plant. The water that come out of the plant don’t take part in the metabolism process.
Benefits of Transpiration to Plants
As any other process there are pros and cons of transpiration too. I’ll list the advantages of this process to plants below.
- Plant becomes cool all the time.
- Large amount of water gets into the plant.
- Distribution of water is throughout the plant.
- Some substances are transported to upper regions of the plant.
- Harmful effects of evaporation to plant leaves is minimized.
- Due to the amount of water absorbed the osmotic pressure of cells is maintained.
What Factors Affecting Transpiration?
Do you remember the factors of photosynthesis process? Anyway, Transpiration too have its own factors which affects the process. Since the water is coming out as vapor, every factor of evaporation too affects the transpiration process.
Here are the factors which affect the evaporation of water,
– Speed of wind.
– Intensity of light.
– Humidity of atmosphere.
– Pressure of atmosphere.
– Temperature of environment.
In addition to above factors, soil and water also has an effect on this process. In order to test the necessity of these factors you must measure the transpiration rate. There is a laboratory instrument known as Potometer to measure the rate of transpiration.
The twig you’re going to use for this experiment must be cut – Using a sharp knife – and fitted inside the water of Potometer. It is required to do this to avoid any air particles entering inside the twig. Small air bubble needs to be allowed to enter capillary tube.
Okay, when the water gets evaporated, the air bubble in the capillary tube will move towards the twig. You can measure the distance moved by the air bubble to find the rate of transpiration. This apparatus could be used to measure the transpiration rate in various environmental situations.
1. Speed of Wind
Water particles around the plant leaves get blown away with the wind. The result is more water particles joining to the atmosphere. The diffusion rate of water increases as the wind speed increases, so the transpiration rate too increases according to the speed of the wind.
2. Intensity of Light
You know that the photosynthesis process happens in the daylight. It requires the energy of sunlight. In the daylight period the stomata gets opened and that causes to increase in the rate of transpiration. So when the light intensity increases transpiration rate too increases.
3. Humidity of Atmosphere
Atmosphere is sometimes cool and sometimes hot, that’s because of the humidity of air. When the air is cool it means the increase of humidity and that’s where the diffusion of water is less from plant leaves. When it is decreased water molecules could easily get into the air.
Therefore, the rate of transpiration decreases when the humidity of the atmosphere increases.
4. Pressure of Atmosphere
Rate of evaporation of a liquid increases in a vacuum, because the pressure is low. That explains when the pressure of atmosphere is low the rate of transpiration increases.
5. Temperature of Environment
Evaporation rate of water increases with the increase of temperature. Atmosphere can hold high amount of water vapor with the temperature. Okay, that means when the environmental temperature increases the transpiration rate too increases.
How Plants Reduce The Rate of Transpiration?
The water enters to the plant from the soil through roots and they leave the plant through plant leaves by transpiration. However the land plants usually don’t get enough water supply, a good example is Xerophytes. Nature gave some adaptations to such plants as mentioned below.
1. Sunken Stomata
Plants which show this adaptation have their stomata hidden or located at low level than the epidermis cells. Due to the fact that they are sunk, they don’t have any direct contact with atmospheric air. So the effect of the environmental factors is little and the transpiration is reduced as a result.
2. Thick Cuticle Formation
Some plants have thick cuticle formed in their leaves. These leaves have a shiny and waxy leaf blade that cover the effect of transpiration factors. Hence the rate is very low.
3. Having Fleshy Stems, Dropping of Leaves & Leaves Turning to Thorns
Some plants such as Cactus, Euphorbia don’t have any leaves. There are plant leaves that falls away when they are young. Some thorns are the conversions of leaves and auxiliary buds.
All these plants have low transpiration rate due to no leaves. You can see plants with fleshy stem and they have a milky white thick liquid that keeps water behind it.
4. Bristles on Leaf Surface
Plants which shows this adaptation have hair like bristles on the leaf surface. These bristles are formed by the epidermis cells. Wet air strata can be seen in between the bristles. That’s what helps plant with this adaptation to reduce the transpiration rate.
5. Rolling of Leaves
Have you come across plants which closes their leaves when touched? This rolling of leaves adaptation is something similar to that. In dry climate plants like grass roll in and cover the stomata. There are many stomata in the upper surface and this rolling technique can reduce the rate of transpiration nicely.
6. Deciduousness
Deciduousness means the dropping of leaves in certain seasons of the year. Plants use this adaptation usually drop their leaves in dry season. No leaves equal to very less transpiration.
Guttation
Guttation is similar to transpiration, but there are differences too. Small holes can be seen in the tip of the tiny veins known as Hydathodes. You know the water entering from the roots go higher areas by some help with the root pressure. That pressure causes the water to go out through those Hydathodes.
This process known as the Guttation. It is the reason why you can see water droplets at the tip of leaf blades.
Scientists have found the only function of Hydathodes is the Guttation.
Root pressure cannot push water in large height trees, therefore Guttation occurs only on small plants.
Example Plants for Guttation,
– Grass
– Alocasia
– Amorph Phallus






Leave a Reply