Humans belong to the natural classification group of Animals. Almost all animals have blood inside their bodies. There are 4 types of animal tissues as Muscle Tissue, Nerve Tissue, Epithelial Tissue and finally Blood Tissue. So that means today I’m going to go deeper about the blood tissue of human beings.
Sometimes we all face to common things in our life. One such thing is getting a wound on hands or legs. I’m sure you have had a wound or at least a bruise in your body. What happens as soon as you’re wounded? Blood comes out of that wound quickly.
Blood is always flowing through the blood vessels inside our body. Blood is a homogeneous fluid and it gets separated into 2 components when left in a test tube. These are 2 components of blood. One component looks dark red gelatinous and the other is a yellow colored fluid.
Okay, how much blood do you have in your body? It’s about 5.5 liters of blood in a normal person. Let’s go deeper and deeper on components of blood!
Components of Blood
You know that every tissue is made up of cells and they are very tiny structures that you can’t see with naked eye. Therefore, you have to get the help of a microscope to observe the components of blood. All you need is a slide of blood kept under the microscope.
You would see lots of cells floating here and there in a fluid when looking at the slide through microscope. Most of these cells are red color. You can see other type of cells which are in different sizes and small in amount.
Now cover the blood slide with a cover slip and add a little drop of dilute Acetic Acid. Then look at the blood slide again through microscope and you’ll see those red blood cells are gone. Instead you can see other type of blood cells, they are white blood cells.
Okay, let me explain each of these 2 blood types and other components of blood in detail now.
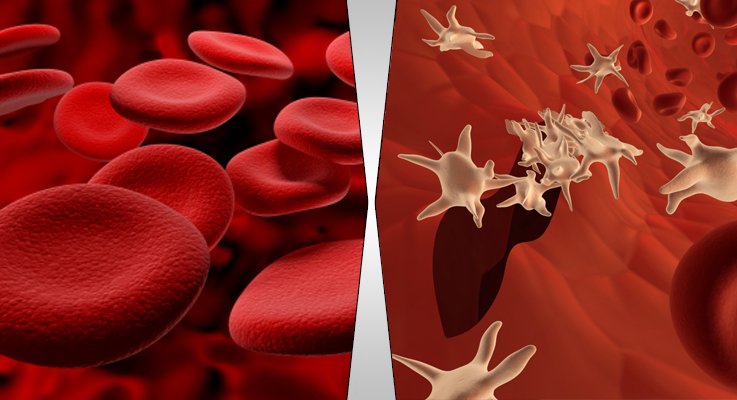
Red Blood Cells or Erythrocytes
The red color cells seen in the above experiment are known as red blood cells, red blood corpuscles or Erythrocytes. Your blood looks red because of red blood cells. Erythrocytes have a bi-concave shape with a movement in group or single inside blood vessels.
Result is the efficient exchange of gases through their surface. Red blood cells are bigger in size, hence they cannot move through capillary tubes easily. That leads to a better exchange of gases in terms of time.
Red color of the red blood cell is coming from hemoglobin. Hemoglobin is made from a pigment known as Haematin that consist of iron and a protein named Globulin. Life is short and red blood cells prove that statement again due to their lifetime is limited to 3 months.
Once reached that time they are broken down in the liver and spleen. Even though the red blood cells died, body can absorb its proteins and iron of the Hemoglobin. Red blood cells are formed in the bone marrow.
OxyHemoglobin is formed by the oxygen and hemoglobin in red blood cells. That resulted in a bright red for the blood. Oxyhemoglobin breaks when they reach cells to release the oxygen and these oxygen diffuses into the cell.
White Blood Cells or Leukocytes
As mentioned earlier, white blood cells are larger than the red blood cells, however the amount of white blood cells is low. If you want that in numbers, the amount of Leukocytes is 1 per 600 Erythrocytes in a person’s body. White blood cells are colorless and have a nucleus.
You can find 4000 to 11,000 white blood cells in a 1ml of human blood. If you read our previous post about animal tissues, you know there are 2 types of white blood cells according to the availability of granules in the cytoplasm. They are Granulocytes and Agranulocytes.
Above 2 types can be divided to another 5. Lympocytes are one type of white blood cells and they have a large nucleus that fills the whole cell with a rounded shape. As erythrocytes these leukocytes are formed in the bone marrow.
Certain leukocytes display an amoeboid movement, they engulf bacteria and viruses that enter to your body. This process of killing bad stuffs is known as Phagocytosis. Sometimes these cells form antibodies against harmful bacteria and viruses.
Platelets
Main components of the blood are erythrocytes and leukocytes. In addition to those, there are another type of cells which are very small and no nuclei. These cells have granules and known as Platelets. If you’re injured the blood comes out of your wound.
Blood will not come out of the wound continuously due to the blood clotting process. Few substances support the blood clotting process and it is quickened by Platelets.
Blood Plasma
When you observe the blood slide through microscope, you saw a fluid around the blood cells. It is the blood plasma which shows a yellow color. Blood plasma contain 55% of the blood and 92% of the plasma is water. Many substances required by the body can be found in the blood plasma.
Blood got a fluid nature because of blood plasma. It transports all the substances such as blood cells, hormones, nutrients and excretory substances throughout the body. It also regulates the body temperature.
These are the components of blood that you can’t see with a quick glance. They are doing an amazing job, isn’t it? I’d like to hear your opinion about these blood components. As a reminder your share is very valuable to me. So please do share 🙂





does nucleus support life of cell??
Yes! It is.
yes it supports