Biology defines 3 types of living organisms as plants, animals and microorganisms. We as humans and all other multicellular organisms such as dogs, birds also fall into Animals group. According to the Cell Theory, the basic unit of structure and function of a living being is the cell. That explains all the living beings are made of cells.
We call group of cells as tissues, hence there is something for you to learn as Animal Tissues and Plant Tissues, but now you’re going to read about Animal Tissues.
Main Types of Animal Tissues
Collection of organized cells that work towards a specific function to a complete organ can be known as a tissue. There are 4 types of main animal tissues inside our bodies. They are,
- Blood Tissue
- Muscle Tissue
- Epithelial Tissue
- Nerve Tissue
However, this post will explain only the blood, muscle and epithelial tissues in detail. Here are few interesting facts about these 4 animal tissues.
- Your blood is a liquid tissue.
- 40% of an animal’s weight is coming from muscle tissue.
- Muscle tissue has the ability of contraction.
- Internal and external surface covering layer is known as epithelial tissue.
- Nerve tissue is made by nerves or nerve cells.
- Nerve cells carry the nervous impulses.
Blood Tissue
Blood tissue contains all the blood in a living body. This tissue contains a number of blood cells namely red blood cells and white blood cells. Blood tissue is in a packing tissue known as Plasma which is a liquid of pale straw color.
This packing tissue – Plasma – contains 90% of water and 10% of various other substances as suspension. Water is very essential for the plasma to translocate the substances around the body. The translocation substances include,
- Globulin
- Prothombin
- Fibrinogen
- Plasma Protein
- Mineral Salts
Remember, substance known as Prothombin takes a major part in blood clotting process. You may have noticed that the blood coming from a wound stops after a while. That is because a blood clot has been created in surface of the wound.
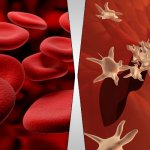
Your blood is red color because of red cells. It has been found that 1mm3 of blood consists of 5 Million – Yep! 5,000,000 – red blood cells. Usually a drop of blood has 50mm3 in volume. These numbers alone mention the high value of red blood cells.
Major job of red blood cells are grabbing the oxygen from lungs and taking them to the tissues. Have you ever wondered why the red blood cells have the red color at all?
Yeah! I guess so, red color is due to a pigment called Hemoglobin dissolved in it. Since red blood cells don’t have nucleus, Hemoglobin has more room to play around within the cell. Origin of the red blood cells are from bone marrow and they die in the spleen.
As you know the other type of blood is white blood cells and there are about 5 types of white blood cells too. However the main 2 types are the Granulocytes and Agranulocytes.
There is one more constituent in the blood tissue, it is Platelets which are covered by membranes. These are fragments of cells and don’t have a nuclei. Just like Prothombin, Platelets also helps in the process of blood clotting. Around 250,000 platelets contained in 1mm3 of human blood.
Similar to red blood cells, platelets also born from bone marrow and die in the spleen.
Below is a quick glance of 5 types of white blood cells.
Blood Constituent
Granulocytes
- Nutrophils
- Eosinophils
- Basophils
Function of Constituent
Defeats bacteria & germs. Allergic responses.
- Produces anti-clotting protein called Heparine.
- Produces chemical to stimulate the tissue damage repair called Hisstamine.
Agranulocytes
- Monocytes
- Lympocytes
Muscle Tissue
If you’re a guy, then you may be really motivated to build a muscular body and build strength. 🙂 All those are possible thanks to muscle tissue in your body.
There are 3 types of muscle tissues in all the animal tissues and you’ll learn them shortly. As previously mentioned muscle tissue has the ability of contraction and expansion. That’s what makes you move of one part of the body relative to the other part.
Stratified Muscle Tissues
These muscles are identified as skeletal or voluntary muscles. Stratified muscles have Dark Miofibril bands and Light Miofibril bands in the cell plasma and these can be seen with naked eye. Due to the attachment of these muscles to the skeleton system, the name skeletal muscles is used.
You can voluntarily move these muscles any time, hence the other name comes to it.
Striated muscles are made up of bundles of fibers which are connected to Perimysium fibers surrounded by Epimysium connective tissues. Once the stimulus understood, the contraction occurs rapidly and fatigue quickly.
Unstriated Muscle Tissues
These are introduced as unstriated muscles because there are no strips in these muscles. Unstriated muscles also known as involuntary muscles or smooth muscles. These are elongated cells with a nucleus surrounded by a small sarcoplasm. Other areas of the cell is made up with flexible fibers running along the cells and connected lightly.
You can find the unstriated muscles in the walls of organs such as intestine and gall bladder. These muscles are helping to send the material through the systems.
Also they are fatigue slowly and contracting slowly with a longitudinal contraction.
Cardiac Muscle Tissues
If you want to know an organ made up of cardiac muscles, then I’d surely mention the heart, because it is purely composed with these muscles. Cardiac muscles too have important features like other 2 types of muscle tissues.
These aren’t divided as uni-nucleus cells. You can see a sarcolemma and cross-striations around the fibers. However, the fibers are not too long as skeletal muscles, but the strips are visible. Cardiac muscles can be contracted as well as removed from the body and they don’t fatigue easily.
The dark bands called intercalated discs are located individually.
Epithelial Tissue
As you know epithelial tissue covers the surfaces of internal and external organs of an organism. A basement membrane made of collagen fiber network is where the bottom layer of cells rest. It is a thin and soft membrane.
Epithelial cells don’t have a direct contact with blood. Below are the 7 types of epithelial tissue. Before that I’d mention the 2 main divisions of epithelial tissue according to the number of layers available.
- Simple Epithelium Tissue
- Compound Epithelium Tissue
We can further divide these 2 main types to 7 as mentioned earlier. First, I’ll explain the 5 simple epithelium tissues.
Simple Epithelium Tissue
Squamous Epithelium
Squamous epithelium can be found in areas such as alveoli of the lungs, kidney renal capsules and the capillary walls of the blood. Squamous epithelium tissue is not very thick, so that it permits diffusion of materials through it.
Cuboidal Epithelium
Cuboidal epithelium forms a lining of ducts such as thyroid, sweat, salivary and urinary collecting ducts in the kidney. These tissue cells have spherical shape nucleus in the center of the cell. It is founded that cuboidal epithelium tissues are performing the functions of absorption and secretion of glands or organs.
Columnar Epithelium
Columnar epithelium tissue cells are narrow and very tall. You can’t find the nucleus of these epithelial cells in an exact place, because they are situated in random places of the cells. You can find columnar epithelium tissue from stomach to rectum.
Again, this tissue also do the functions of secretion and absorption, but in the stomach area which means digestion of foods.
Ciliated Epithelium
Ciliated epithelium can be found in the respiratory passages like trachea, nostrils and tracheoles. Function of this tissue is to capture the particles when passing through above areas. You can see cilia formed in the surface of the cells of ciliated epithelium tissue.
Pseudostratified Epithelium
Pseudostratified epithelium can be found lining in areas such as trachea, urinary tract and upper respiratory tract. This layer of cells are attached to the basement membrane, however not all the cells reach the free surface.
Compound Epithelium Tissue
Stratified Epithelium
Stratified epithelium is designed with combination of few cell layers. Therefore, this issue is very thick, rough as well as can resist the friction. Germinal layer is the innermost cell layer of this tissue. Outer layer becomes a dead layer where it is peeling off naturally and flaking away.
As you have guessed it, stratified epithelium tissue can be found in your external body such as skin and internal body such as buccal cavity and esophagus.
Transitional Epithelium
Transitional epithelium tissue cells can be modified in many shapes as they can stretch and contract. These are found in the uretus, urinary bladder and urethra. There is a another name for this tissue as Urothelium.
Finally, as a summary of everything above, we can list the following points.
- Tissues can be defined as collections of cells specialized in performing particular functions.
- Animal tissues do a valuable service in labor of division.
- There are few types of tissues according to the structure and functions they perform.


Hello!
friend that is very nice
from Nigerians